Evaluation of Associated Changes on the Uterus and Fallopian Tube Histology in Response to Graded Doses of Syzygium aromaticum (Clove) in Wistar Rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26538/tjdr/v2i3.1Keywords:
Wistar Rats, Histology, Fallopian Tube, Uterus, Syzygium aromaticumAbstract
Purpose: Syzygium aromaticum (Clove) is used as a preservative, as well as in the preparation of various spicy foods. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of graded doses of cloves on the uterus and fallopian tube histology using Wistar rats as experimental animal model.
Method: Twenty (20) Wistar rats after two weeks of acclimatization were assigned into four groups (I, II, III and IV) of five animals each. Group I served as the control group and received normal saline, while Groups II, III, and IV received 2 mL, 4 mL, and 6 mL of clove extract once daily for 30 days. The body weights of the rats were monitored over the treatment period. At the end of the experimental period, the animals were fasted for 12 hours and thereafter were sacrificed, and their uterus and fallopian tubes were harvested and used for histological examination.
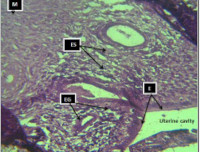
Results: Syzygium aromaticum extract exhibited dose-dependent effect on the histoarchitecture of the female reproductive tissues, particularly, the uterus and fallopian tubes in Wistar rats. Low and moderate doses of the extract appeared to maintain normal tissue architecture, while high doses resulted in mild degenerative changes.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that a high dose of Syzygium aromaticum has the potential to cause mild structural changes in the histoarchitecture of the female reproductive tissues, particularly, the uterus and fallopian tube.
Downloads
References
1. Batiha GES, Beshbishy AA, Tayebwa DS, Shaheen MH, Yokoyama N, Igarashi I. Inhibitory effects of Syzygium aromaticum and Camellia sinensis methanolic extracts on the growth of Babesia and Theileria parasites. Ticks Tick. Borne Dis. 2019; 10:949–958. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2019.04.016
2. Pandey VK, Srivastava S, Ashish, Dash KK, Singh R, Dar AH, Singh T, Farooqui A, Shaikh AM, Kovacs B. Bioactive properties of clove (Syzygium aromaticum) essential oil nanoemulsion: A Comprehensive Review. Heliyon. 2023; 10(1):e22437. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22437.
3. Amitava K and Rohitas D. A review on Chinese herbal medicine used as carminative. Pharmacol Res Mod Chin Med. 2024; 11:100409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prmcm.2024.100409.
4. RuiXuan L, YunTian L, JinYing M, Qi Z, Yudong S, Jiashan L, Hongjiao L, Hongjiao, TianYi Z. Traditional Chinese Medicine for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Narrative Review of the Evidence and Potential Mechanisms Involving the Brain-Gut Axis. Front Pharmacol. 2024; 15: 1444922. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1444922
5. Lone ZA and Jain NK. Phytochemical Analysis of Clove (Syzygium aromaticum). Dried Flower Buds Extract and its Therapeutic Importance. J Drug Deliv Ther. 2022; 12(4-S):87-92.
6. Ahmad MF, Zahoor M, Hasan S, Ali M, Gulzar F, Singh R. Clove: a valuable natural product for human welfare. Int J Nutr Pharm Neurol Dis. 2016; 6(3):69-76.
7. Siddiqui MJ, Ismail M, Khan AA, Haque SE. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of clove oil from Syzygium aromaticum L. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2011; 24(2):269-277.
8. Pramod K1, Ansari SH, Ali J. Eugenol: a natural compound with versatile pharmacological actions. Nat Prod Commun. 2010; 5(12):1999-2006.
9. Al-Snafi AE. The pharmacological importance of Syzygium aromaticum - A review. IOSR J Pharm. 2019; 9(8):25-36.
10. Mahmood T, Akhtar N, Khan, BA. Synergistic effect of clove oil and its major compounds with antibiotics against oral bacteria. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015; 28(3):1023-1028
11. Prabuseenivasan S, Manickkam J, Savarimuthu I. In vitro antimicrobial activity of some plant essential oils. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2006; 6:39.
12. Prakash D and Gupta C. Anti-oxidative effect of eugenol on ameliorating hepatic oxidative stress in wistar rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010; 48(9):2200-2205.
13. Bethesda. P. Amoxicillin-Clavulanate. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-. Amoxicillin. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548517/.2020.
14. Janka B, Jones B, Anita FR. Mitigation of interfacial dielectric loss in cloves-on silicon superconducting quibits, Chambers University of Technology. 2023; 41299p.
15. El-Raouf OA, Onoja SM, Ahmed MB. The effect of clove (Syzygium aromaticum) on uterine histomorphology and sexual hormones in adult female rats. Eur J Biomed Pharm Sci. 2019; 6(10):160-164.
16. Tanko Y, Okasha MA, Kamal Z, et al. Evaluation of uterine toxicity of Zingiber officinale, Syzygium aromaticum and Moringa oleifera in female Wistar rats. J Biol Agric Healthc. 2019; 5(9)123-127.
17. Sharma P, Gayasuddin M, Singh S. Effect of Clove Extracts on Histologic Features of the Hartmann’s Solution Induced Endometriosis in Albino Mice: An Experimental Study. Malay J Med Sci. 2020; 27(3):95-103.
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.




